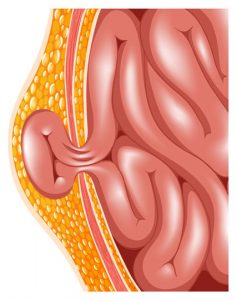
Diverticulosis – Treatment
In most cases, a high-fiber diet and the occasional mild painkillers will help relieve symptoms. Sometimes, an episode of diverticulitis is severe enough to require hospitalization and possibly surgery.
Increasing the amount of fiber in the diet can reduce the symptoms of diverticulitis and prevent complications such as diverticulitis. Fiber keeps stools soft and reduces pressure within the colon to facilitate movement of the bowel contents. The American Dietetic Association recommends an intake of 20 to 35 grams of fiber daily.
The table below shows the amount of fiber in some foods that you can easily add to your diet.
| Portion size | Quantity in fiber | |
| Fruit | ||
| Apple | 1 medium size = | 4 grams |
| Peach | 1 medium size = | 2 grams |
| Pear | 1 medium size = | 4 grams |
| Mandarin | 1 medium size = | 2 grams |
| Vegetables | ||
| Asparagus, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 1.5 grams |
| Broccoli, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 2 grams |
| Brussels sprouts, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 2 grams |
| Cabbage, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 2 grams |
| Carrot, fresh, cooked | 1= | 1.5 grams |
| Cauliflower, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 2 grams |
| Lettuce | 1= | 1 gram |
| Spinach, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 2 grams |
| Tomato, raw | 1= | 1 gram |
| Pumpkin, fresh, cooked | 1= | 2.5 grams |
| Starchy vegetables | ||
| Black beans, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 4 grams |
| Lima beans, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 4-5 grams |
| Kidney beans, fresh, cooked | ½ cup | 6 grams |
| Potatoes, fresh, cooked | 1= | 3 grams |
| Grains | ||
| Bread, whole-wheat | 1 slice | 2 grams |
| Brown rice, cooked | 1 cup | 3.5 grams |
| Cereal, brown flakes | ¾ cup | 5 grams |
| Oatmeal, plain, cooked | 1 cup | 3 grams |
| White rice, cooked | 1 cup | 1 gram |
Until recently, many doctors recommended avoiding foods with small seeds, such as tomatoes or strawberries, because they believed that some particles could become trapped in the diverticula and cause inflammation. This, however, is now a controversial issue and no findings support this view. The amounts and types of food one can eat vary from person to person.
If cramping, bloating and constipation are problems, the doctor may prescribe short term medication with painkillers. Many medications, however, affect colonic motility and emptying, an undesirable side effect for people with diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis
Treatment for diverticulitis focuses on clearing the infection and inflammation, resting the colon and preventing or minimizing complications. An attack of diverticulitis without complications can respond to antibiotics within a few days if they are taken in time.
To rest the colon, the doctor may recommend bed rest and a liquid diet, combined with pain medication.
An acute episode with severe pain or severe infection may require hospitalization. More acute cases of diverticulitis are treated with antibiotics and a liquid diet. Antibiotics are administered by intravenous injection. In some cases, however, surgery may be necessary.