What is Crohn’s disease?
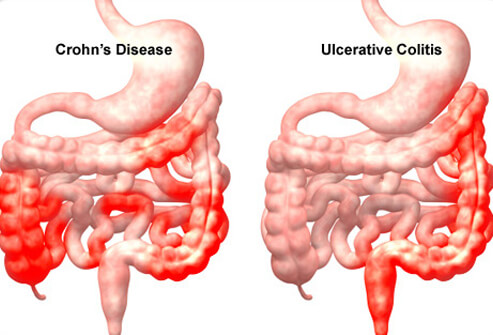
Crohn’s disease causes inflammation in the small intestine. It usually occurs in the lower part of the small intestine, called the ileum, but it can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. The inflammation extends deep into the layers of the damaged organ. It can cause pain and lead to frequent bowel movements, resulting in diarrhea.
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which is the general name for conditions that cause inflammation in the intestines. Unfortunately, it can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are similar to other intestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome and another type of IBS called ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis causes inflammation and ulcers in the inner lining of the wall of the colon, the mucosa.
Crohn’s disease affects men and women equally and there appears to be heredity. About 20% of people with Crohn’s disease have a blood relative who has some form of PD. Most commonly, a brother or sister and sometimes a parent or child. Crohn’s disease is also called ileitis or enteritis.
What causes Crohn’s disease?
There are many theories about what causes Crohn’s disease, but none has been proven. The most popular theory holds that the body’s immune system reacts to a virus or bacteria causing progressive inflammation in the gut. Crohn’s disease sufferers tend to have immune system disorders, but doctors do not know if these are the result or cause of the disease. What is certain is that Crohn’s disease is not caused by emotional stress.